

Then, copy the TCP.SequenceNumber = sequence filter from the client trace and paste it on the server trace.
Reset ip fast windows#
To understand how TCP works, see The three-way handshake via TCP/IP and Description of Windows TCP features. The retransmission of a frame happens if no acknowledgment of the sequence is received. This result shows that the original frame #441 isn't received by the server and is retransmitted by the sender. The complete TCP sequence with this sequence number is displayed as follows: Right-click the SequenceNumber in Frame Details and select Add Selected Value to Display Filter.ĭisable the previous filter by adding "//" as follows: Use the same TCP sequence number (2278877548) to identify this frame. To analyze an ETL file, go to Tools > Options > Parser Profiles > Windows > Set As Active > OK.Īs shown in the screenshot, frame #441 is retransmitted twice, which means it is transmitted by the sender three times. Run the following command: NETSH TRACE START CAPTURE=YES REPORT=DISABLED TRACEFILE=.ETL MAXSIZE=512 You can also use the Windows built-in capturing tool as follows: Start logging with Microsoft Network Monitor or Wireshark to capture traffic on both endpoints. Steps to take logs with network packet capturing tools To get a packet level log analysis, check underlying network issues by using a network packet capturing tool (such as Microsoft Network Monitor, Wireshark, or ctsTraffic).
Reset ip fast how to#
This section describes how to check for underlying network issues while measuring a throughput baseline or troubleshooting throughput issues. RSS can also be enabled by using the PowerShell cmdlet: Set-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name -RegistryKeyword *RSS -RegistryValue 1
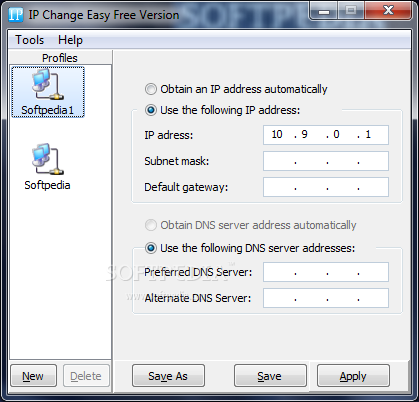
Use Command Prompt to enable the autotuning level Use Windows Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell to enable the option by setting the TCP receive window autotuning level. That's because the TCP Window Scale option isn't enabled on either server. The throughput measured with the ctsTraffic tool is lower than the baseline. Two servers located in different sites are connected over a high latency network. Slow throughput speed on a high latency and bandwidth network Slow throughput on low latency and high bandwidth network.Slow throughput on high latency and high bandwidth network.This article describes the following TCP/IP performance issues: You can review Part 1: TCP/IP performance overview and Part 2: TCP/IP performance underlying network issues.
This article is included in a 3-part series.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
